Vertical Hydroponic Systems: A Complete Overview

Introduction
Vertical hydroponic systems offer a transformative approach to gardening, ideal for space-limited urban settings or indoor environments where traditional gardening is a challenge. These systems utilize vertical space and significantly reduce water usage, highlighting their sustainability and efficiency. Popular methods like Deep Water Culture (DWC), Aeroponics, and Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) are specifically well-suited for vertical integration due to their effective use of space and resource management.
Setting up these systems involves an array of equipment, including pumps, lighting, and automated nutrient delivery systems, which are essential for creating a thriving vertical garden. Regular maintenance such as monitoring pH levels, adjusting nutrient solutions, and system cleaning is crucial to prevent common problems like algae growth and nutrient deficiencies. Knowing how to troubleshoot these issues quickly and effectively ensures the longevity and productivity of the garden.
The following sections will delve into each hydroponic system type, discussing their suitability for vertical gardening, the setup process, detailed maintenance tips, and practical troubleshooting guides. This comprehensive overview will equip you with the knowledge to choose, implement, and sustain the right hydroponic system for your vertical gardening needs, ensuring a thriving, lush garden regardless of space constraints.
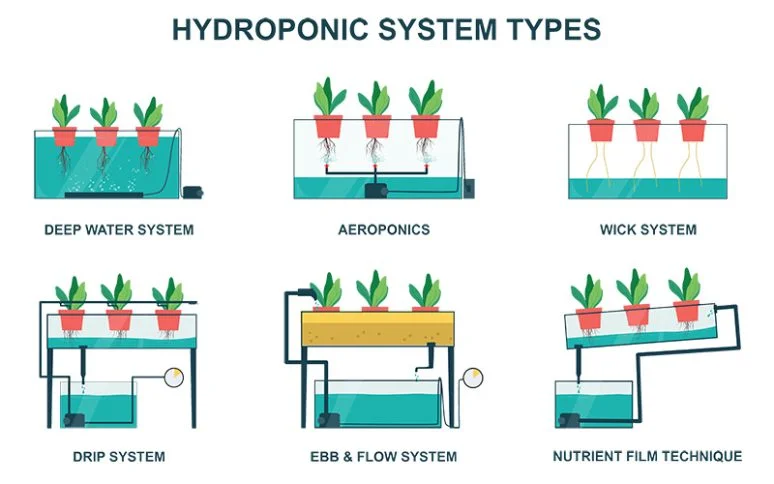
Exploring Types of Hydroponic Systems
In hydroponics, plants receive their nutrients from a water-based solution, which eliminates the need for soil. This method is renowned for reducing water usage by up to 90% compared to traditional gardening, as the closed system recirculates water and nutrients. This approach not only saves a significant amount of water by recycling it through the system but also promotes faster growth and yields due to the direct delivery of nutrients to the roots. In fact, plants in hydroponic setups tend to mature up to 25% faster, resulting in more frequent and abundant harvests.
Deep Water Culture (DWC): Benefits for Vertical Gardens
Deep Water Culture is a hydroponic favorite, especially beneficial for vertical gardens due to its simplicity and effectiveness. In DWC, plants float in a nutrient-rich solution with their roots submerged, allowing for robust growth. This system is ideal for large fast-growing plants and leafy greens, providing a stable and abundant water supply that boosts growth without the need for complex recirculating systems.
Aeroponics: Advanced Technology for Vertical Gardens
Aeroponics is the cutting edge in hydroponic technologies, where plants grow with their roots suspended in air and misted with a nutrient solution. This system is incredibly water-efficient and perfect for vertical settings, as it minimizes the need for growing medium and reduces the weight load. Aeroponics also promotes faster growth and higher yields, making it ideal for herbs and leafy greens.
Fogponics: Cutting-edge Mist Solutions for Vertical Cultivation
Fogponics is a variation of aeroponics that uses a nutrient-rich fog to hydrate and feed plants. This method allows for an even distribution of nutrients and moisture, crucial for tight vertical spaces. Fogponics systems are particularly effective for delicate plants that benefit from gentle feeding methods.
Wick System: Simplicity and Reliability in Vertical Setups
The Wick System is one of the simplest hydroponic setups, using a wick to draw nutrient solution from a reservoir to the plant roots. It’s perfect for beginners and can be easily implemented in vertical gardens. This system is low-maintenance and reliable, suitable for smaller plants that require less nutritional intake.
Drip System: Integration and Efficiency in Vertical Farming
The Drip System method drips nutrient solution directly to the roots of each plant, making it highly efficient and water-conservative. It’s particularly well-suited for large vertical installations as it can be precisely controlled, ensuring that each plant receives the exact amount of nutrients it needs. This method reduces waste and maximizes the use of nutrients and water.
Ebb & Flow System: Timing and Flood Management in Vertical Gardens
The Ebb & Flow System works by flooding the plant root zone with a nutrient solution at regular intervals, which then drains back into the reservoir. This method is great for vertical setups with larger plants, as it ensures thorough watering and nutrient distribution, but requires precise timing and control to prevent over watering.
Nutrient Film Technique (NFT): Continuous Nutrient Delivery in Vertical Systems
Nutrient Film Technique uses a shallow stream of water containing all the dissolved nutrients required for plant growth. It flows over the roots of plants, which are held in a slight incline. NFT is highly efficient for space in vertical gardens, allowing for close planting and high productivity, especially suitable for leafy greens and herbs.
Aquaponics: Combining Aquaculture and Hydroponics Vertically
Aquaponics merges hydroponics with fish farming, where fish waste provides nutrients for the plants, and the plants purify the water for the fish. This symbiotic system is not only efficient but also organic and sustainable. In vertical gardens, aquaponics can be a space-saving solution that yields both edible plant crops and fish.
Each method has its specific benefits and suitability for different plant types and environmental conditions. Whether you are looking to enhance a commercial space or simply add greenery to your home, vertical hydroponic systems offer a versatile and efficient solution.
Equipment Needed for Vertical Hydroponic Systems
Essential Equipment for Vertical Hydroponic Gardens
To establish a successful vertical hydroponic system, several key pieces of equipment are necessary:
Pumps: Required to circulate the nutrient solution through the system, ensuring that your plants receive adequate water and nutrients.
Reservoirs: Store the nutrient solution. They should be sized appropriately based on the number of plants and the type of hydroponic system being used.
Pipes or Tubes: Used to transport the nutrient solution to the plants and return it to the reservoir.
Grow Lights: Provide necessary light spectrum for plant growth, especially vital in indoor settings or areas with limited natural sunlight.
Timers: Automate the feeding and lighting cycles, critical for maintaining consistent conditions within the system.
pH and EC Meters: Monitor the acidity and nutrient strength of your solution to ensure plants receive the optimal growing environment.
Growing Medium: Supports the plants in the absence of soil; choices include rockwool, clay pellets, or peat moss, depending on the system design.
Special Considerations for Vertical Installations
When setting up a vertical hydroponic system, there are specific considerations to keep in mind to maximize the system’s effectiveness and maintain plant health:
Structural Support: Ensure that your vertical system is structurally sound to support the weight of water, plants, and equipment, particularly as plants grow larger.
Space Efficiency: Design your setup to make the best use of available vertical space, which might include using tiered systems or rotating gardens.
Water Distribution: Pay attention to how water is delivered to the top of the system and ensure it evenly reaches all plants as it moves downward.
Access and Maintenance: Set up your system so that all plants are easily accessible for pruning, harvesting, and monitoring for pests or diseases.
Light Distribution: Position grow lights strategically to ensure all plants receive equal light, preventing the lower plants from being shaded by those above.
By carefully selecting and configuring the equipment and considering the unique aspects of vertical installations, gardeners can create highly productive and space-efficient hydroponic systems.
Maintaining Your Vertical Hydroponic Garden
Routine Checks and Maintenance Tasks
Maintaining a vertical hydroponic garden involves consistent monitoring to ensure optimal growth conditions. Regularly check the system for any leaks or blockages, which could affect water flow and nutrient delivery. Inspect plant roots for health; they should be white and vigorous, not brown or slimy. Replace any failed lights immediately to prevent affecting plant growth cycles. It’s also crucial to verify that timers and monitoring systems are functioning correctly to maintain the automated processes essential for plant care.
Monitoring and Adjusting Nutrient Levels
Keeping nutrient levels in check is vital for the health of your hydroponic garden. Use pH and EC meters to test the water regularly—ideally daily, but at least twice a week. The ideal pH level for most hydroponic systems is between 5.5 and 6.5. Adjustments might be necessary depending on the readings, which can be done using pH up or down solutions. Additionally, replenish the nutrient solution completely every two to three weeks to prevent nutrient imbalances and build-up of salts.
Importance of System Cleaning and Algae Control
Cleaning is an essential part of maintaining a hydroponic system. Every few weeks, flush the system with clean water to remove any salt build-up, which can be toxic to plants. It’s important to clean and sterilize all parts of the system, such as reservoirs, pipes, and pumps, between crop cycles to prevent the spread of pathogens. Controlling algae is another critical aspect, as algae can block light from reaching the roots and use up nutrients necessary for plant growth. Keep the system’s water levels and surfaces clean, and consider covering any exposed surfaces to prevent light from promoting algae growth.
Troubleshooting Common Problems in Vertical Hydroponic Systems
Identifying and Addressing Common Issues
Vertical hydroponic systems can encounter specific problems that need immediate attention to prevent crop loss. One common issue is inadequate nutrient delivery, often indicated by yellowing leaves or stunted growth, which might suggest a blockage or malfunction in the nutrient delivery system. Root rot is another frequent challenge, recognizable by brown, mushy roots, usually caused by poor aeration or excessive water levels. Pests and diseases, such as aphids or fungal infections, can also thrive in the warm, moist environments of hydroponic systems.
Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Guide for Specific Systems
Deep Water Culture (DWC): If plants show signs of distress, check the oxygen levels in the water first. Increasing aeration with additional air stones or a more powerful air pump can resolve many issues related to oxygen starvation. Also, regularly clean the system to prevent the buildup of decaying plant matter, which can deplete oxygen levels and promote bacterial growth.
Nutrient Film Technique (NFT): Ensure that the nutrient film remains shallow; too much water can drown the roots, while too little can cause drying out. Check for clogs or sediment build-up in the channels that could impede flow and rectify immediately.
Aeroponics: The most common issue is nozzle clogging, which can halt the misting process, quickly leading to root drying. Regular cleaning of nozzles and filters will help maintain proper function. Monitoring and adjusting the misting frequency and duration can also prevent over or under-watering.
Ebb & Flow System: Timing is critical. If plants are wilting, adjust the flood and drain cycles to ensure that roots are not submerged for too long, leading to potential root rot, or too briefly, causing dehydration. Check the timer and pump regularly to ensure they operate as set.
In each case, preventative maintenance is as crucial as responsive measures. Regularly check all components of your system, clean and replace parts as necessary, and always ensure your plants have the optimal growing environment by monitoring system conditions closely. This proactive approach can prevent many common problems from developing and ensure your vertical hydroponic garden remains healthy and productive.
Choosing the Right System for Your Needs
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Hydroponic System
Choosing the right hydroponic system for your needs depends on several key factors:
Type of Plants: Different plants have different needs; leafy greens might thrive in NFT systems, while larger fruiting plants do better in DWC systems.
Space Availability: Vertical systems can vary significantly in their space requirements. Systems like aeroponics and NFT are great for tight spaces, as they utilize vertical height effectively.
Climate Control: Consider the environment in which you are growing. Systems that recirculate air and water efficiently might be necessary in hotter or more humid climates to prevent plant stress.
Expertise Level: Some systems require more technical knowledge and maintenance. Beginners might start with simpler systems like the wick or deep water culture, whereas more experienced growers might opt for NFT or aeroponics.
Budget: Initial setup costs can vary greatly. Evaluate your budget to determine which system provides the capabilities you need without overspending.
Comparing Systems for Efficiency, Cost, and Space Requirements
Deep Water Culture (DWC): High efficiency, low cost, moderate space. Ideal for beginners and scalable for larger operations.
Nutrient Film Technique (NFT): Moderate efficiency, moderate cost, requires less space vertically. Suitable for commercial growers focusing on leafy greens.
Aeroponics: High efficiency, higher cost, minimal space. Best for growers who can invest more upfront for increased growth rates and yields.
Ebb & Flow: Moderate efficiency, variable costs, moderate space. Versatile for various plant types but requires careful water management.
Fogponics: Similar to aeroponics with slightly higher efficiency, potentially higher costs, minimal space. Offers delicate nutrient delivery ideal for sensitive plants.
By carefully assessing your needs against these criteria, you can select the hydroponic system that best suits your growing goals, ensuring that you maximize your garden’s productivity and efficiency.
Implementation and Setup Guide
Step-by-Step Instructions on Setting Up a Vertical Hydroponic System
Choose the Location: Select a space with sufficient light, access to water, and protection from extreme weather conditions. An indoor setting often requires artificial lighting.
Select Your System Type: Decide based on your needs, expertise, and the types of plants you wish to grow. Aeroponics, DWC, or NFT systems are popular choices for vertical setups.
Install the Frame: Set up the vertical structure or shelving unit where the plants will be housed. Ensure it is sturdy enough to support the weight of the system including water and plants.
Set Up the Water Reservoir: Place a large enough reservoir at the base of the system to ensure a continuous supply of nutrient solution.
Install Pumps and Irrigation Lines: Connect a pump to the reservoir to circulate the nutrient solution through the system. Arrange the irrigation lines so that each plant will receive adequate nutrients.
Arrange the Plants: Insert plants into the system, ensuring they are securely placed within the grow medium.
Add Nutrients and Water: Fill the reservoir with the appropriate water and nutrients. Test the pH and adjust as necessary.
Set Up Lighting and Timers: If indoors, install grow lights above the plants, ensuring even coverage. Use timers to automate the light cycles and irrigation schedules.
Tips for Efficient Layout and Space Management
Maximize Vertical Space: Utilize wall-mounted or freestanding vertical grow towers to optimize the use of vertical space effectively.
Organize for Accessibility: Arrange plants in a manner that allows easy access for maintenance tasks such as pruning, harvesting, and monitoring plant health.
Use Modular Components: Opt for modular hydroponic systems that can be easily expanded or reconfigured as your garden grows or your needs change.
Consider Plant Growth: Place taller plants on the upper tiers and shorter or hanging plants lower down to ensure all plants receive sufficient light and air circulation.
Streamline the System: Minimize the distance between the reservoir and the highest point of the system to reduce the load on the pump and improve the efficiency of nutrient delivery.
Implementing these steps will help establish a successful vertical hydroponic garden that is not only productive but also space-efficient and easy to manage.
Conclusion
Vertical hydroponic systems offer an ingenious solution for maximizing gardening potential in minimal spaces, revolutionizing how we think about urban and indoor agriculture. These systems leverage the vertical dimension, introducing a sustainable, efficient way to cultivate plants by saving water, space, and enhancing growth rates. From the water-saving prowess of aeroponics and nutrient film techniques to the ease of maintenance in wick and deep water culture systems, the variety of methods available allows gardeners to tailor their setups based on specific needs and constraints.
By understanding the essential equipment required, from pumps to grow lights, and implementing the system with a focus on effective layout and space management, even novice gardeners can achieve thriving gardens in constrained environments. Regular maintenance and the ability to troubleshoot common issues ensure these systems continue to operate at their best, promoting a robust and continuous yield.
Whether you’re looking to enhance a home environment, start a small-scale commercial operation, or simply experiment with advanced gardening techniques, vertical hydroponic systems present a viable and dynamic avenue. Armed with this knowledge, you can choose, install, and maintain a system that not only meets your gardening goals but also pushes the boundaries of what’s possible in modern agriculture.